Air Conditioner Repair Techniques: "Touch, Look, Listen, Check, Analyze"
2024-07-30
The air conditioner is composed of the refrigeration system and the electrical system. The causes of faults can be divided into two categories: one is the external cause or human-made fault, and the other is the internal fault.
When analyzing and dealing with faults, the external causes should be excluded first. After eliminating the external factors, the internal faults can be further divided into two types: refrigeration system faults and electrical system faults. Generally, the electrical system faults should be excluded first. As for the electrical system faults, they can be searched from the following two aspects: whether the switching power supply is supplying power; whether the motor winding is normal. According to the above general analysis ideas, the fault range can be gradually narrowed, and the cause of the fault will naturally become clear.
When the refrigeration system is running, the methods of asking, touching, looking, listening, and checking are adopted for the initial check. These methods are simple and effective.
When analyzing and dealing with faults, the external causes should be excluded first. After eliminating the external factors, the internal faults can be further divided into two types: refrigeration system faults and electrical system faults. Generally, the electrical system faults should be excluded first. As for the electrical system faults, they can be searched from the following two aspects: whether the switching power supply is supplying power; whether the motor winding is normal. According to the above general analysis ideas, the fault range can be gradually narrowed, and the cause of the fault will naturally become clear.
When the refrigeration system is running, the methods of asking, touching, looking, listening, and checking are adopted for the initial check. These methods are simple and effective.
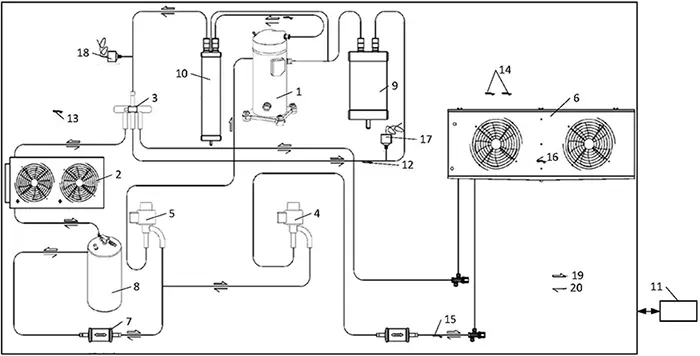
Touch
- After the compressor operates normally for 20 - 30 minutes, touch the temperatures of the suction pipe, exhaust pipe, compressor, air outlet of the evaporator, condenser and other parts. The quality of the refrigeration effect can be judged by the hand feeling.
- Touch the temperature of the compressor casing: generally at 90 - 100℃.
- Touch the surface temperature of the evaporator: The temperatures at all parts of the evaporator of a normally working air conditioner should be the same. Its surface is cool, generally about 15 degrees. There is condensate water at the exposed copper pipe elbow.
- Touch the surface temperature of the condenser: After the air conditioner starts to operate, the condenser will heat up quickly. The faster it heats up, the faster the refrigeration is. Under normal use, the temperature of the condenser can reach about 80 degrees, and the wall temperature of the condenser tube is generally 45 - 55℃.
- Touch the surface temperature of the low-pressure return gas pipe: Normally, the suction pipe is cold and the exhaust pipe is hot. It should feel cool when touched by hand. If the ambient temperature is low, there will also be condensate water on the surface of the low-pressure return gas pipe. If the return gas pipe does not condensate, while the high-pressure exhaust pipe is relatively hot and the compressor casing is also very hot, it is likely that the refrigerant is insufficient. If the entire return gas pipe of the compressor is condensated and reaches half or all of the compressor casing, it indicates that there is too much refrigerant.
- Touch the temperature of the high-pressure exhaust pipe: It should feel relatively hot when touched by hand, and it is even hot to the touch in summer.
- Touch the surface temperature of the drying filter: Under normal circumstances, touching the surface of the drying filter by hand feels slightly higher than the ambient temperature. If there is a cool feeling or condensate, it indicates that the drying filter has a slight blockage.
- Touch the temperature at the air outlet: The hand should feel a little cool when the wind comes out, and it will feel a little cold if the hand stays for a long time.
Look
- Check whether the high and low pressure values are normal.
- First, check whether the appearance of the air conditioner is intact and whether each component is working normally.
- Check whether there are any fractures in the pipelines of the refrigeration system and whether there are any oil traces at each welding point. Oil traces at the welding points may indicate leakage.
- Check whether the inserts of the electrical components are loose, whether the positions of each connecting copper pipe are correct, and whether there is any copper pipe touching the casing.
- Check whether the runout of the centrifugal fan blade and the axial flow fan blade is too large, and whether there is obvious vibration in the motor and the compressor.
- Check the frosting situation of the low-pressure part of the capillary. During normal refrigeration, at the beginning of the compressor operation, the capillary will frost a thin layer, and then gradually melt away. However, insufficient refrigerant or pipeline blockage will cause the frosting not to melt. If there is frost on the pipe section from the capillary outlet to the entrance of the outdoor heat exchanger and the other parts are dry, it indicates that the capillary is half-blocked. Superficially, the phenomena of insufficient refrigerant and half-blockage are the same.
Listen
Listen carefully to whether the sound of the entire machine operation is normal. When the air conditioner is operating, it will make certain sounds. But if some abnormal sounds are heard, there is a problem. For example, when listening to the compressor operation, if there is a "buzzing" sound, it can be immediately determined that it is the sound that the compressor motor cannot start normally. At this time, the power should be turned off immediately to find the cause.
The "hissing" sound is the high-pressure airflow sound after the high-pressure damping tube in the compressor breaks;
The "tapping" sound is the metal collision sound inside the compressor;
The "clanging" sound is the impact sound after the suspension spring in the compressor falls off or breaks.
The "thumping" sound is the liquid hammer sound of the compressor, that is, the impact sound of a large amount of refrigerant being sucked into the flywheel keyway of the compressor with loose fit. In addition, other noises can also be judged by hearing, such as: the sound of the split axial flow fan hitting the iron sheet of the casing. The "squeaking" sound of the fan due to lack of oil; the sound of the compressor bottom corner bolts loosening and vibrating; the sound of the capillary touching the casing.
Listen carefully to whether the sound of the entire machine operation is normal. When the air conditioner is operating, it will make certain sounds. But if some abnormal sounds are heard, there is a problem. For example, when listening to the compressor operation, if there is a "buzzing" sound, it can be immediately determined that it is the sound that the compressor motor cannot start normally. At this time, the power should be turned off immediately to find the cause.
The "hissing" sound is the high-pressure airflow sound after the high-pressure damping tube in the compressor breaks;
The "tapping" sound is the metal collision sound inside the compressor;
The "clanging" sound is the impact sound after the suspension spring in the compressor falls off or breaks.
The "thumping" sound is the liquid hammer sound of the compressor, that is, the impact sound of a large amount of refrigerant being sucked into the flywheel keyway of the compressor with loose fit. In addition, other noises can also be judged by hearing, such as: the sound of the split axial flow fan hitting the iron sheet of the casing. The "squeaking" sound of the fan due to lack of oil; the sound of the compressor bottom corner bolts loosening and vibrating; the sound of the capillary touching the casing.
Check
When the ambient temperature is around 30℃ (under the air conditioning refrigeration condition), if the pressure of the low-pressure gauge (gauge pressure) is below 0.4MPa, it indicates that the refrigerant is insufficient or there is a leakage. The normal value of the pressure of the high-pressure gauge (gauge pressure) should be around 2MPa. Both too high or too low indicate abnormalities. If the outlet of the condenser is blocked, the high-pressure pressure can increase, while the low-pressure pressure decreases. The conventional items for inspection and observation are as follows:
When the ambient temperature is around 30℃ (under the air conditioning refrigeration condition), if the pressure of the low-pressure gauge (gauge pressure) is below 0.4MPa, it indicates that the refrigerant is insufficient or there is a leakage. The normal value of the pressure of the high-pressure gauge (gauge pressure) should be around 2MPa. Both too high or too low indicate abnormalities. If the outlet of the condenser is blocked, the high-pressure pressure can increase, while the low-pressure pressure decreases. The conventional items for inspection and observation are as follows:
- Low-pressure pressure; high-pressure pressure; equilibrium pressure when stopping;
- Suction pipe temperature; exhaust pipe temperature; compressor temperature;
- Condenser; evaporator; filter; capillary;
- Working current; working voltage.
Analysis
After one look, two touches, three listens, and four measurements, further analyze the location of the fault and the severity of the fault. Since the refrigeration system, the electrical system, and the air circulation system are all connected and influence each other, they should be analyzed comprehensively. The actual location of the fault should be judged from the surface to the inside, and a clear mind should always be maintained. So as not to be negligent for a moment, make a wrong judgment, and cause unnecessary losses.
After one look, two touches, three listens, and four measurements, further analyze the location of the fault and the severity of the fault. Since the refrigeration system, the electrical system, and the air circulation system are all connected and influence each other, they should be analyzed comprehensively. The actual location of the fault should be judged from the surface to the inside, and a clear mind should always be maintained. So as not to be negligent for a moment, make a wrong judgment, and cause unnecessary losses.
Related Articles
- Influence of Fin Spacing of Evaporator in Air Cooler on Frost Formation
- Air - side Economizer
- Winter Approaches: How to Solve the Low High - pressure Issue of Air - cooled Condensing Units?
- What Are the Common Causes of Cold Air Blower Noise?
- How to Troubleshoot and Repair High - pressure Protection of Air - cooled Units?
- What Exactly Are the Ten Typical Malfunctions of Air Conditioners?
- What Misconceptions Should Be Avoided in Low - temperature Refrigeration System Repairs
- Practical Knowledge on Freeze Protection of Air - conditioning Equipment
- Remember! 3 Steps to Calculate Central Air - conditioner Cooling Capacity
- How to Read the High - and Low - Pressure Gauges of Refrigeration Air - conditioners?
- Analysis of Seven Reasons for Ice Formation in Computer Room Air Conditioners
- Air - conditioner Low - pressure Alarm? These Nine Common Causes
- Selection of Bypass Control Valves for Air - conditioning Water Systems
- Common Faults and Solutions of Central Air - conditioning Chiller Units
- Could a Tiny Copper Tube Cause a Multi - split Air Conditioner to Stop Cooling? Refrigeration Workers Must Pay Attention!
- Maintenance Techniques for Air - conditioning Refrigeration Systems
- Considerations in Selecting Packaged Air Conditioners and Their Heat Recovery Operations
- Characteristics and Differences among Water System, Air System and Refrigerant System
