The principle of air conditioning refrigeration
2024-07-23
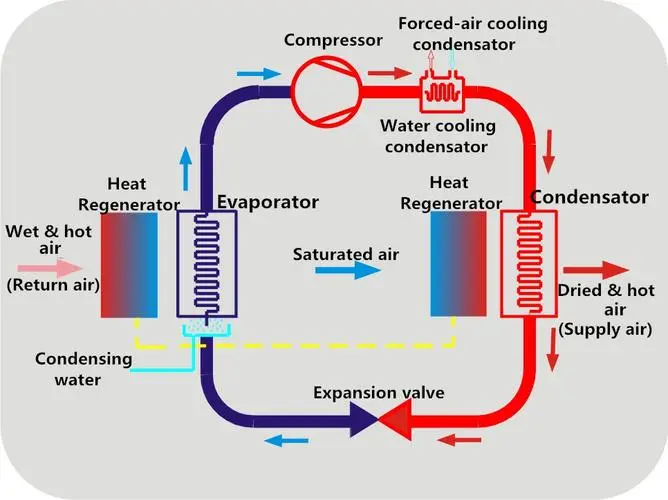
The compressor compresses the gaseous refrigerant into a gaseous state of high temperature and high pressure and sends it to the condenser for cooling. After cooling, it becomes a liquid refrigerant of medium temperature and high pressure and enters the drying bottle for filtering and dehumidification. The medium-temperature liquid refrigerant is throttled and depressurized by the expansion valve (throttling component) into a gas-liquid mixture of low temperature and low pressure (with more liquid). It absorbs the heat in the air through the evaporator and vaporizes into a gaseous state, and then returns to the compressor for continuous compression and continues the refrigeration cycle. During heating, there is a four-way valve that makes the flow direction of Freon in the condenser and evaporator opposite to that during refrigeration. Therefore, during heating, cold air is blown outdoors and hot air is blown by the indoor unit.
Related issues
Air conditioning aging
The service life of large household appliances is generally about 15 years. Although some reports claim that some brand air conditioners can still work normally after 20 years of use, this is actually very rare. When the air conditioner is used beyond its service life, many faults will occur, and even if it is repaired, problems will continue to arise.
Solution: Purchase a new air conditioner
The service life of large household appliances is generally about 15 years. Although some reports claim that some brand air conditioners can still work normally after 20 years of use, this is actually very rare. When the air conditioner is used beyond its service life, many faults will occur, and even if it is repaired, problems will continue to arise.
Solution: Purchase a new air conditioner
Air conditioning low on Freon
A common reason for an air conditioner not cooling is the lack of Freon, often referred to as a lack of refrigerant. If you find that the cooling effect of your air conditioner at home is not as good as before, it is mostly because the refrigerant is insufficient or leaked. Solution: This reason for non-cooling mostly occurs in air conditioners that have been used for three or four years. Most of it is a normal phenomenon and is the normal consumption of the air conditioning refrigerant (that is, the Freon or refrigerant we often refer to) due to long-term use. But this only shows that the cooling is not as good as before, and it will not completely not cool. Because the pressure is insufficient and it does not deviate too much from the normal value. At this time, you only need to find a regular maintenance outlet to add it; of course, sometimes it is because of the installation reason or the reason of the machine itself that the refrigerant is leaked. This is a common and relatively easy-to-find reason, and this kind of problem is also relatively easy to handle. Check the pressure with a pressure gauge and add if it is insufficient.
Solution: Add Freon
A common reason for an air conditioner not cooling is the lack of Freon, often referred to as a lack of refrigerant. If you find that the cooling effect of your air conditioner at home is not as good as before, it is mostly because the refrigerant is insufficient or leaked. Solution: This reason for non-cooling mostly occurs in air conditioners that have been used for three or four years. Most of it is a normal phenomenon and is the normal consumption of the air conditioning refrigerant (that is, the Freon or refrigerant we often refer to) due to long-term use. But this only shows that the cooling is not as good as before, and it will not completely not cool. Because the pressure is insufficient and it does not deviate too much from the normal value. At this time, you only need to find a regular maintenance outlet to add it; of course, sometimes it is because of the installation reason or the reason of the machine itself that the refrigerant is leaked. This is a common and relatively easy-to-find reason, and this kind of problem is also relatively easy to handle. Check the pressure with a pressure gauge and add if it is insufficient.
Solution: Add Freon
Insufficient power of the air conditioner
Some friends buy an air conditioner with a small number of horsepower to place in a very large room in order to save money. Originally, the power of the small-horsepower air conditioner is insufficient. Although the power of the air conditioner and the area of the room seem to be matched, due to the relatively unsealed room or the presence of heat sources in the room (many computers). Of course, the exposure of the glass room is also one of the heat sources, etc. This kind of situation is usually easily ignored by us. If these reasons are found and well handled, not only can the air conditioner cool better, but it can also save electricity and extend the service life of the air conditioner.
Solution: Generally, it can only start from increasing the number of air conditioners (to match the refrigeration area required in practice with the refrigeration area under the jurisdiction of the air conditioning power); changing the conditions of the usage environment; increasing the sealing of the usage environment; reducing the heat sources in the air conditioning usage environment, etc. to solve the problem of non-cooling.
Some friends buy an air conditioner with a small number of horsepower to place in a very large room in order to save money. Originally, the power of the small-horsepower air conditioner is insufficient. Although the power of the air conditioner and the area of the room seem to be matched, due to the relatively unsealed room or the presence of heat sources in the room (many computers). Of course, the exposure of the glass room is also one of the heat sources, etc. This kind of situation is usually easily ignored by us. If these reasons are found and well handled, not only can the air conditioner cool better, but it can also save electricity and extend the service life of the air conditioner.
Solution: Generally, it can only start from increasing the number of air conditioners (to match the refrigeration area required in practice with the refrigeration area under the jurisdiction of the air conditioning power); changing the conditions of the usage environment; increasing the sealing of the usage environment; reducing the heat sources in the air conditioning usage environment, etc. to solve the problem of non-cooling.
Excessive ambient temperature
This non-cooling situation is common when our outdoor unit is installed in a relatively closed space or the temperature around the outdoor unit is too high. In this way, it is extremely easy that the air in the small space where the outdoor unit is located does not circulate, resulting in the heat dissipated by the radiator not being able to flow away and causing the air conditioner not to cool; Another common statement is that when the outdoor temperature exceeds 43 degrees, most air conditioners have difficulty transferring the indoor heat to the outside through the radiator of the outdoor unit, which will also cause the air conditioner not to cool.
Solution: Change the usage environment of the outdoor unit (move away from the high-temperature environment or make the surrounding air of the outdoor unit more easily circulate)
This non-cooling situation is common when our outdoor unit is installed in a relatively closed space or the temperature around the outdoor unit is too high. In this way, it is extremely easy that the air in the small space where the outdoor unit is located does not circulate, resulting in the heat dissipated by the radiator not being able to flow away and causing the air conditioner not to cool; Another common statement is that when the outdoor temperature exceeds 43 degrees, most air conditioners have difficulty transferring the indoor heat to the outside through the radiator of the outdoor unit, which will also cause the air conditioner not to cool.
Solution: Change the usage environment of the outdoor unit (move away from the high-temperature environment or make the surrounding air of the outdoor unit more easily circulate)
The connecting copper pipe is too long
The overly long copper pipe increases the transmission distance, resulting in a decrease in the cooling effect of the air conditioner.
Solution: Try to shorten the length of the copper pipe between the outdoor unit and the indoor unit of the air conditioner.
The overly long copper pipe increases the transmission distance, resulting in a decrease in the cooling effect of the air conditioner.
Solution: Try to shorten the length of the copper pipe between the outdoor unit and the indoor unit of the air conditioner.
Long-term lack of cleaning and maintenance
Because the outdoor unit is installed outdoors, it is easy to be overlooked. After long-term use, the outdoor unit will adsorb a lot of dust and debris on the radiator and other dirt, so the heat dissipation effect of the radiator is poor and the air conditioner does not cool. In addition, long-term use of the air conditioner without cleaning and maintenance will lead to unhygienic room air, easily cause air conditioning diseases, increase power consumption, and shorten the service life of the air conditioner.
Solution: Regularly clean and maintain the air conditioner.
Because the outdoor unit is installed outdoors, it is easy to be overlooked. After long-term use, the outdoor unit will adsorb a lot of dust and debris on the radiator and other dirt, so the heat dissipation effect of the radiator is poor and the air conditioner does not cool. In addition, long-term use of the air conditioner without cleaning and maintenance will lead to unhygienic room air, easily cause air conditioning diseases, increase power consumption, and shorten the service life of the air conditioner.
Solution: Regularly clean and maintain the air conditioner.
Refrigeration principle
The compressor compresses the gaseous Freon into a gaseous Freon of high temperature and high pressure, and then sends it to the condenser (outdoor unit). After heat dissipation, it becomes a liquid Freon of normal temperature and high pressure. Therefore, the outdoor unit blows out hot air. The liquid Freon passes through the capillary and enters the evaporator (indoor unit). The space suddenly increases and the pressure decreases. The liquid Freon vaporizes and becomes a gaseous Freon of low temperature, thereby absorbing a large amount of heat. The evaporator cools down. The fan of the indoor unit blows the indoor air through the evaporator. Therefore, the indoor unit blows out cold air; When water vapor in the air encounters a cold evaporator, it condenses into water droplets and flows out along the water pipe. This is the reason why the air conditioner discharges water. Then the gaseous Freon returns to the compressor for continuous compression and continues the cycle. During heating, there is a component called a four-way valve that makes the flow direction of Freon in the condenser and evaporator opposite to that during refrigeration. Therefore, during heating, cold air is blown outdoors and hot air is blown by the indoor unit. In fact, it uses the principle learned in junior high school physics that heat is released when liquefaction (from gas to liquid) and heat is absorbed when vaporization (from liquid to gas).
The compressor compresses the gaseous Freon into a gaseous Freon of high temperature and high pressure, and then sends it to the condenser (outdoor unit). After heat dissipation, it becomes a liquid Freon of normal temperature and high pressure. Therefore, the outdoor unit blows out hot air. The liquid Freon passes through the capillary and enters the evaporator (indoor unit). The space suddenly increases and the pressure decreases. The liquid Freon vaporizes and becomes a gaseous Freon of low temperature, thereby absorbing a large amount of heat. The evaporator cools down. The fan of the indoor unit blows the indoor air through the evaporator. Therefore, the indoor unit blows out cold air; When water vapor in the air encounters a cold evaporator, it condenses into water droplets and flows out along the water pipe. This is the reason why the air conditioner discharges water. Then the gaseous Freon returns to the compressor for continuous compression and continues the cycle. During heating, there is a component called a four-way valve that makes the flow direction of Freon in the condenser and evaporator opposite to that during refrigeration. Therefore, during heating, cold air is blown outdoors and hot air is blown by the indoor unit. In fact, it uses the principle learned in junior high school physics that heat is released when liquefaction (from gas to liquid) and heat is absorbed when vaporization (from liquid to gas).
Refrigeration principle of lithium bromide air conditioning Here, the refrigeration principle of lithium bromide air conditioning is particularly proposed. Different from the compression-type air conditioning, the working fluid used in absorption refrigeration is usually a binary solution composed of two substances with different boiling points. Among them, the substance with a low boiling point is the refrigerant and the substance with a high boiling point is the absorbent. Therefore, the binary solution is also called the refrigerant - absorbent working fluid pair. The so-called binary solution refers to a mixture composed of two substances that do not chemically react with each other. Various physical properties (such as pressure, temperature, concentration, etc.) of this homogeneous mixture are exactly the same throughout the mixture and cannot be separated into the original constituent substances by purely mechanical precipitation or centrifugation.
Its refrigeration principle is divided into two parts
Its refrigeration principle is divided into two parts
- The binary solution is heated and boiled in the generator by the heat source, generating refrigerant vapor which is condensed into refrigerant liquid in the condenser. The liquid refrigerant enters the evaporator after throttling through the U-shaped tube and is sprayed under low-pressure conditions in the evaporator. The liquid refrigerant evaporates, absorbs the heat of the refrigerant, and produces a refrigeration effect.
- The concentrated solution flowing out of the generator, after being cooled and depressurized by the heat exchanger, flows into the absorber by itself and mixes with the original solution of the absorber to become a concentrated solution of an intermediate concentration. The intermediate concentration solution is conveyed and sprayed by the absorber pump and absorbs the refrigerant vapor coming out of the evaporator to become a dilute solution. The dilute solution is delivered to the generator by the generator pump and is reheated by the heat source to generate refrigerant vapor again to form a concentrated solution and enter the next cycle period. In summary, any refrigeration equipment is composed of four major parts (compressor, condenser, evaporator, throttling device). The refrigerant absorbs or releases heat through physical state changes in the refrigerator to achieve the effect of refrigeration or heating.
Heating principle
Heat pump heating uses the compression condenser of the refrigeration system to heat the indoor air. When the air conditioner is working for refrigeration, the low-pressure refrigerant liquid evaporates and absorbs heat in the evaporator while the high-temperature and high-pressure refrigerant releases heat and condenses in the condenser. Heat pump heating is achieved by electromagnetic commutation, reversing the positions of the suction and exhaust pipes of the refrigeration system. The indoor coil of the evaporator for the original refrigeration work becomes the condenser during heating. In this way, the refrigeration system absorbs heat outdoors and releases heat indoors to achieve the purpose of heating. The air conditioner is actually controlled by the thermal expansion and contraction of the medium. The indoor part is the contraction and the outdoor part is the expansion. How does the expansion occur? That is, through the compressor compressing the medium to do work, a lot of heat will be generated, which is the expansion. Then, it is transmitted to a space with a much larger volume through a capillary. In this way, the pressure of the medium is much lower at once. This is the contraction and heat absorption, which instantly exchanges the heat in the room into cold gas. Set an appropriate temperature. During refrigeration, do not set the temperature too low. If the room temperature is adjusted to 26 - 27 degrees Celsius, its cooling load can be reduced by more than 8%. Practice has proved that for people sitting or doing light work, when the room temperature is maintained at 28 - 29 degrees Celsius and the relative humidity is maintained at 50 - 60%, people do not feel muggy or sweat. It should fall within the comfort range. When people are sleeping, their metabolic rate decreases by 30 - 50%. The air conditioner can be set to the sleep switch gear and the set temperature is 2 degrees Celsius higher, which can achieve 20% power saving; In winter for heating, if the temperature is set 2 degrees Celsius lower, 10% power can also be saved. Choose an air conditioner with moderate capacity. An air conditioner with insufficient refrigeration capacity not only cannot provide sufficient refrigeration effect but also increases the possibility of usage faults due to the long-term continuous operation of the machine and gives users a poor impression of high power consumption and insufficient power.
Heat pump heating uses the compression condenser of the refrigeration system to heat the indoor air. When the air conditioner is working for refrigeration, the low-pressure refrigerant liquid evaporates and absorbs heat in the evaporator while the high-temperature and high-pressure refrigerant releases heat and condenses in the condenser. Heat pump heating is achieved by electromagnetic commutation, reversing the positions of the suction and exhaust pipes of the refrigeration system. The indoor coil of the evaporator for the original refrigeration work becomes the condenser during heating. In this way, the refrigeration system absorbs heat outdoors and releases heat indoors to achieve the purpose of heating. The air conditioner is actually controlled by the thermal expansion and contraction of the medium. The indoor part is the contraction and the outdoor part is the expansion. How does the expansion occur? That is, through the compressor compressing the medium to do work, a lot of heat will be generated, which is the expansion. Then, it is transmitted to a space with a much larger volume through a capillary. In this way, the pressure of the medium is much lower at once. This is the contraction and heat absorption, which instantly exchanges the heat in the room into cold gas. Set an appropriate temperature. During refrigeration, do not set the temperature too low. If the room temperature is adjusted to 26 - 27 degrees Celsius, its cooling load can be reduced by more than 8%. Practice has proved that for people sitting or doing light work, when the room temperature is maintained at 28 - 29 degrees Celsius and the relative humidity is maintained at 50 - 60%, people do not feel muggy or sweat. It should fall within the comfort range. When people are sleeping, their metabolic rate decreases by 30 - 50%. The air conditioner can be set to the sleep switch gear and the set temperature is 2 degrees Celsius higher, which can achieve 20% power saving; In winter for heating, if the temperature is set 2 degrees Celsius lower, 10% power can also be saved. Choose an air conditioner with moderate capacity. An air conditioner with insufficient refrigeration capacity not only cannot provide sufficient refrigeration effect but also increases the possibility of usage faults due to the long-term continuous operation of the machine and gives users a poor impression of high power consumption and insufficient power.
Related Articles
- Have You Encountered the Three Common Problems of Refrigeration Compressors?
- How to Calculate Refrigeration Load? And What Are the Issues?
- What to Do if the Compressor of a Frozen and Refrigerated Display Cabinet Runs but the Refrigeration Effect Is Poor?
- Instructions for Welding and Drainage in the Installation of Refrigeration Equipment Pipelines
- What to Do if the Compressor of the 【Refrigerated and Frozen Display Cabinet】 Unit Fails to Start?
- Common Pressure Valves and Protection Devices in Refrigeration Units
- Precautions for Using Rotary Refrigeration Compressors
- What Misconceptions Should Be Avoided in Low - temperature Refrigeration System Repairs
- Essential for Maintenance! Parameters and Phenomena of Normal Operation of Refrigeration and Heating Systems
- Composition and Common Faults of Screw Refrigeration Compressors
- How to Read the High - and Low - Pressure Gauges of Refrigeration Air - conditioners?
- What is Cascade Refrigeration?
- Introduction to Control Valves in Refrigeration Systems
- Welding Equipment Used in Refrigeration System Maintenance
- Where Lie the Key Construction Technologies of the Ammonia Refrigeration System?
- What to Do When a Refrigeration Unit Malfunctions?
- Could a Tiny Copper Tube Cause a Multi - split Air Conditioner to Stop Cooling? Refrigeration Workers Must Pay Attention!
- Has Your Refrigeration System Experienced "Oil Carry - over"?
